

Best pH Probes For Hydroponics in 2025 – A Complete Buying Guide
Finding the best pH probe for hydroponics can make or break your growing success. In hydroponics, maintaining the correct pH is essential because it directly
# Type at least 1 character to search # Hit enter to search or ESC to close

No products in the cart.

No products in the cart.
Product Categories

A conductivity test measures a solution’s ability to conduct electricity, reflecting ion concentration. It’s crucial for assessing water quality, ensuring product purity, preventing system damage, and monitoring industrial processes in fields like water treatment, pharmaceuticals, food, and energy.
Conductivity testing is an indispensable analytical tool used across a variety of industries to measure the concentration of ions in a solution, which in turn helps to assess its purity and suitability for different applications. This simple yet powerful test has broad applications, from water quality monitoring to pharmaceuticals, power generation, and even space exploration. But what exactly does conductivity mean, and why is it critical to monitor it across diverse industrial processes?
In this article, we will dive deep into the science of electrical conductivity, the practical applications of conductivity tests, and how these tests are used across industries such as water treatment, food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, power generation, mining, aerospace, HVAC systems, and more.
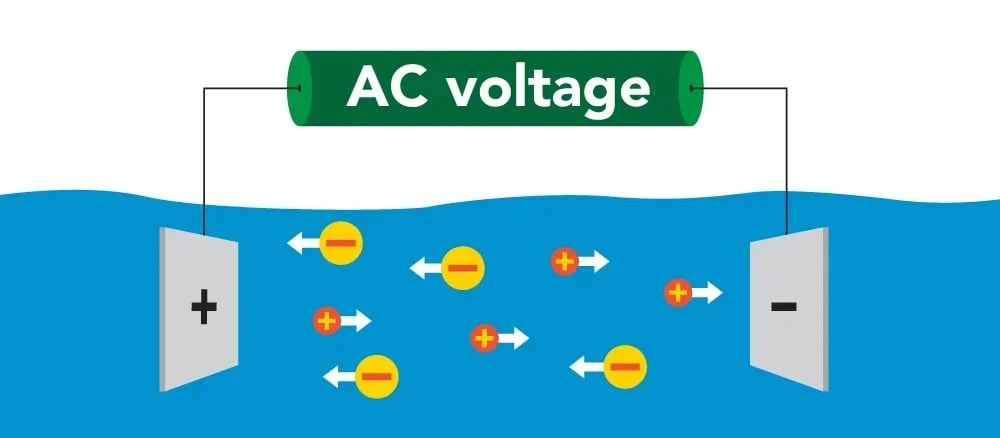
Electrical conductivity (EC) refers to a material’s ability to conduct an electric current. While metals like copper or silver are highly conductive due to the free movement of electrons, aqueous solutions such as water conduct electricity through the movement of ions (charged particles like sodium, chloride, or calcium). The greater the concentration of these ions, the higher the electrical conductivity of the solution.
In solutions, electrical current is carried by ions, such as sodium (Na⁺) or chloride (Cl⁻) ions, which migrate under an electric field. The ability of a solution to conduct electricity depends on:
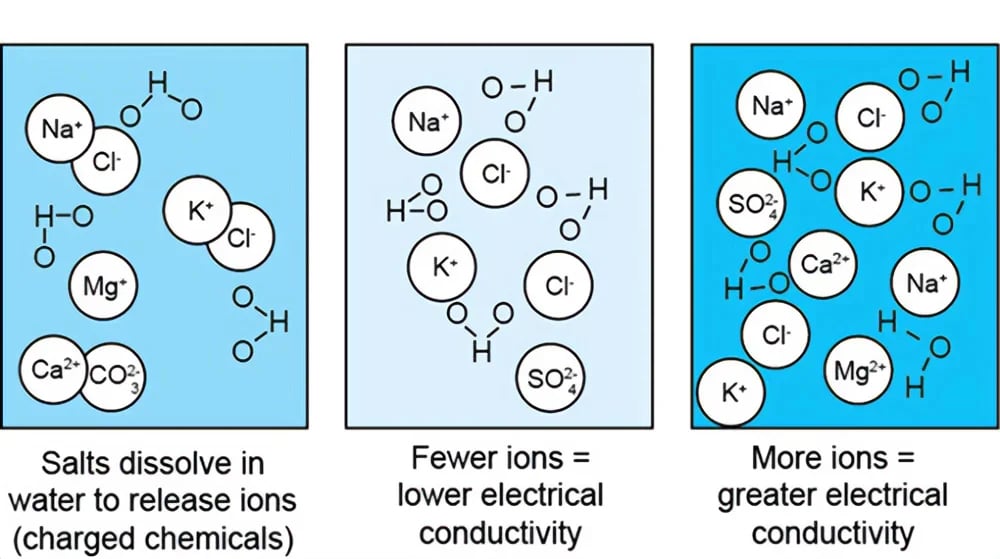
The reciprocal of conductivity is known as resistance, and it is the measure of how much a material resists the flow of electrical current. While conductivity is usually expressed in Siemens per meter (S/m) or milliSiemens per centimeter (mS/cm), its inverse—resistivity—is used in specialized applications like ultrapure water systems.
For most aqueous solutions, conductivity serves as an indirect measure of the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in the solution. Higher TDS levels indicate higher concentrations of dissolved ions, which typically affect the purity and quality of the water.
While conductivity measurement is relatively straightforward, it’s essential to account for temperature effects. As the temperature of a solution increases, the mobility of ions increases, thereby raising the conductivity. To eliminate this variable, conductivity meters often incorporate temperature compensation to standardize measurements at a reference temperature, typically 25°C.
Conductivity testing is important because it provides valuable insights into the purity and chemical composition of a solution. Here are a few reasons why conductivity is crucial:
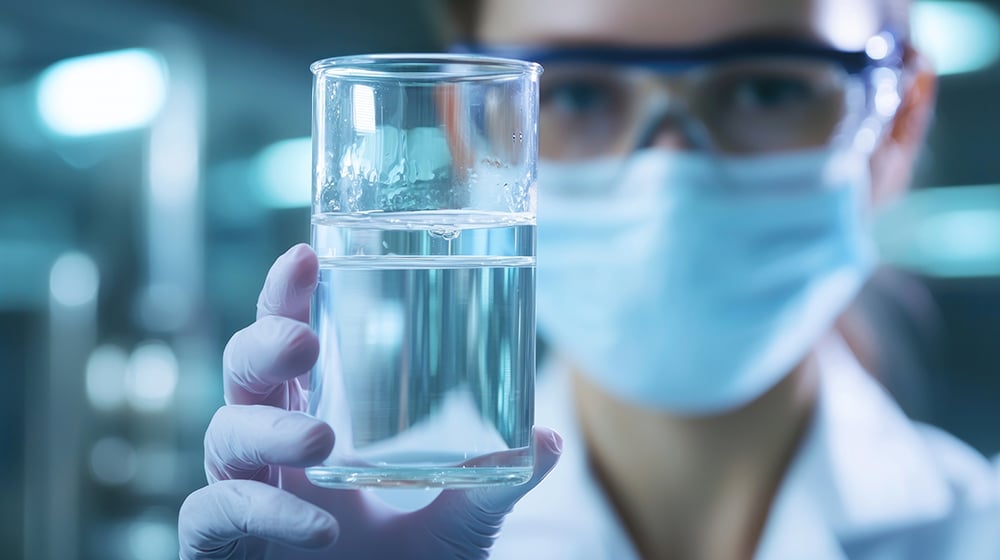
Conductivity testing is critical in water treatment for evaluating water quality, identifying pollution, and managing mineral content. Wastewater treatment plants use conductivity meters to monitor dissolved salts, metals, and chemicals, and detect sudden pollution spikes, which could indicate industrial discharges or contamination.
In desalination processes and water purification methods, conductivity is used to monitor salinity levels in both brine and freshwater outputs, ensuring the efficiency of reverse osmosis (RO) systems. Similarly, demineralization units that remove dissolved solids from water use conductivity readings to ensure that treated water meets the required purity for industrial use.

Key Applications:
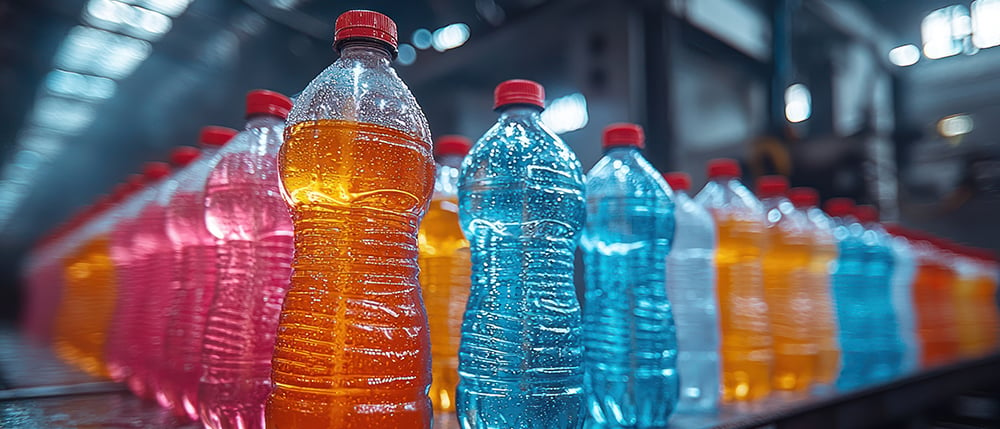
Conductivity testing in the food and beverage industry ensures that the water used in production meets strict quality standards. The conductivity of water can reveal the presence of impurities like salts or chemicals, which can affect the taste, texture, or safety of the final product.
For example, bottled water producers use conductivity testing to ensure their water is within the acceptable conductivity range for mineral content. Similarly, breweries, dairy farms, and soft drink manufacturers rely on conductivity measurements to maintain consistent water quality in their production processes.

Key Applications:
In the pharmaceutical industry, water quality is critical because even small contaminants can affect the efficacy and safety of drugs. Pharmaceutical-grade water, such as Water for Injection (WFI), must meet rigorous purity standards. Conductivity testing is used to ensure the removal of salts and other ions, maintaining the water’s quality throughout production.
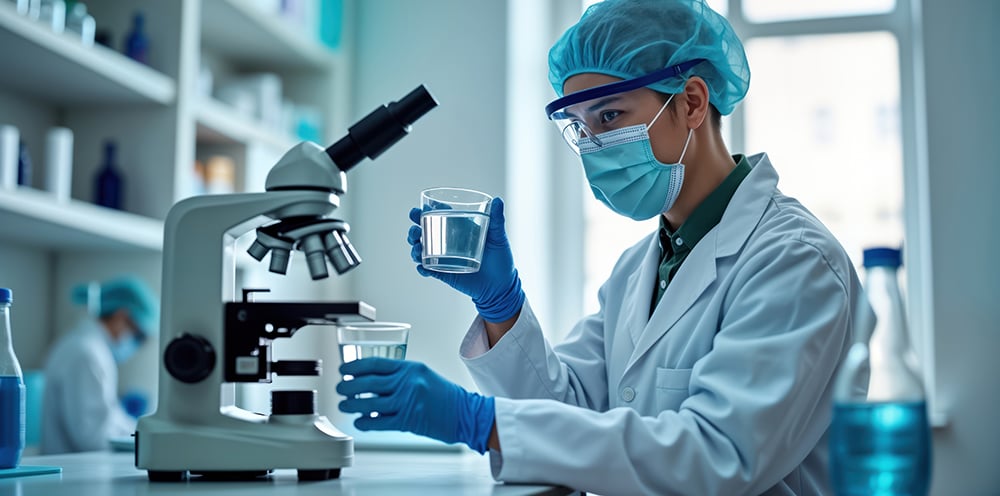

High conductivity readings can indicate contamination, prompting corrective actions to ensure the quality of drug formulations, especially in sterile production environments.
Key Applications:
The chemical industry uses conductivity testing to monitor the composition of chemical solutions, identify impurities, and optimize industrial processes. Whether in chemical streams, reverse osmosis (RO) output or demineralized water, conductivity meters are employed to ensure the required levels of ion concentration are maintained for efficient processing.

For example, in demineralization systems used in power plants or manufacturing, conductivity measurements help monitor ion removal processes. A high conductivity reading can indicate a failure in the demineralization system, signaling the need for maintenance or adjustment.
Key Applications:
In power generation, particularly in steam boilers and condensate systems, conductivity testing is essential for ensuring the quality of water used in cooling and energy production systems. High conductivity levels in boiler feedwater can lead to scaling, corrosion, and efficiency losses.
Monitoring the conductivity of condensate water returning to the boiler helps identify contamination and ensure that the water remains within safe operating limits.

Key Applications:
Conductivity testing is used in mining to monitor water quality and control chemical concentrations during the extraction of metals and minerals. Conductivity measurements help monitor ore leaching solutions, ensuring the right balance of chemicals is present to extract metals efficiently.
In addition, conductivity can provide insights into water quality in mining operations, which is critical to maintaining safe operations and preventing environmental contamination.

Key Applications:
In the aerospace industry, conductivity testing is used to ensure the purity of water used in spacecraft and satellite cooling systems. Ultrapure water (with very low conductivity) is required to prevent any impurities that might affect sensitive components.
Key Applications:
In HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, conductivity sensors monitor heat transfer fluids, such as water mixed with glycol. These systems use conductivity readings to determine the concentration of dissolved ions, which is important for preventing corrosion, scaling, and freeze damage in the system.

Key Applications:
Conductivity testing is a versatile, cost-effective, and crucial tool used across a wide array of industries. From ensuring safe drinking water to optimizing industrial processes, its ability to measure the concentration of dissolved ions plays a key role in maintaining product quality, system efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Whether you’re involved in water treatment, food production, pharmaceuticals, power generation, or aerospace, understanding conductivity and how to accurately measure it can ensure the safety, quality, and success of your operations.
To learn more about conductivity testing or what conductivity meter will best suit your testing needs, do not hesitate to contact the world-class team at Atlas Scientific.

Finding the best pH probe for hydroponics can make or break your growing success. In hydroponics, maintaining the correct pH is essential because it directly

The fastest way to reduce ammonia levels in a fish tank is to perform partial water changes, temporarily stop feeding fish, use chemical filtration, increase
Notifications