

Best pH Probes For Hydroponics in 2025 – A Complete Buying Guide
Finding the best pH probe for hydroponics can make or break your growing success. In hydroponics, maintaining the correct pH is essential because it directly
# Type at least 1 character to search # Hit enter to search or ESC to close

No products in the cart.

No products in the cart.
Product Categories

Sustainable vertical farming maximizes crop yield through stacked layers, using advanced hydroponics and LED lighting to grow crops within limited spaces. This innovative farming method saves water, has reduced transportation emissions, and offers year-round food production even in urban areas.
The global population continues to grow, putting pressure on food production systems. Vertical farming is an alternative to traditional farming methods that offers a promising solution to Earth’s growing population.
Innovative technology is revolutionizing agriculture. Vertical farming has introduced new ways of growing food, relieving the pressure on traditional farming, and helping solve food security issues globally. This article will examine why many farmers are turning to vertical farming and why you may want to change over, too!
Vertical farming is an agricultural technique that involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers. It can be built almost anywhere, from rooftops in densely populated urban areas to inside warehouses, skyscrapers, or on depleted land where soil farming cannot continue.
Vertical farming uses cutting-edge technology you may already be familiar with. The most common include:
Due to the controlled environment, vertical farming is excellent for creating ideal crop growth conditions. Farmers monitor temperature, humidity, lighting, and water supply to maintain these conditions. Specialized equipment such as humidity sensors, temperature sensors, and flow meters are used to check that the system is running correctly.

Traditional farming relies heavily on large areas of arable land, which may not be available in some places (like urban cities and scarce farmland). Vertical farming allows farmers to continue growing crops because it takes advantage of vertical space. It also combines advanced technology with sustainable practices to produce healthy food, regardless of what the weather is doing on the outside.
Vertical farming offers many benefits that address some of the most challenging issues agriculture faces today. From year-round food production to minimizing water use, vertical farming is changing how farmers grow food. Below, we will examine the advantages of vertical farming in greater detail, using technical insights and real-world examples.
One of the most significant advantages of vertical farming is its ability to maximize space. Vertical farms can produce significantly more food per square meter by growing crops in stacked layers than traditional farming methods. This is especially beneficial in densely populated urban areas with limited or unavailable arable land.

For example, a single vertical farm can achieve the exact yield of several acres of conventional farmland, making it a game-changer for regions with limited agricultural space. The efficient use of vertical space also allows for diverse crop production, enabling farms to grow multiple types of plants simultaneously.
One study found that a vertical farm farming lettuce produced up to 80 times the yield per square meter than open-field conventional farming. This is a critical advantage in densely populated urban areas where arable land is scarce or nonexistent.
Examples include Singapore’s Sky Greens, one real-world application in which the whole farm system, albeit on the outskirts, revolves in vertically rotated racks producing leafy greens on a tight plot of space to produce almost a good supply of fresh vegetables for Singapore’s fresh demand.
Vertical farming can grow diverse crops, providing more variability in food and better resilience. Using one facility that grows various plants, from leafy greens to strawberries to medicinal herbs, further contributes to multi-functional and robust farming.
Seasonal changes and weather patterns often limit traditional farming, but vertical farming allows for continuous, year-round production. As mentioned earlier, vertical farms always provide ideal growing conditions by controlling environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity.
The steady production cycle in vertical farming ensures constant supplies of fresh produce and helps increase the stability of food prices due to reduced incidences of food shortages. It also supports local food systems by enabling communities to obtain fresh, nutritious crops regardless of the season.
Leading vertical farming operations utilize advanced climate-control systems to maintain optimal growing conditions 365 days a year, regardless of external weather. Their facilities produce fresh greens throughout the year, even during harsh winters.
This uninterrupted production cycle stabilizes food supply and helps reduce seasonal price fluctuations, benefiting producers and consumers. Moreover, vertical farms can grow crops typically unavailable in certain climates by eliminating seasonal constraints and expanding access to a broader range of fresh produce.

Weather unpredictability and climate change challenge traditional farming and cause it to fail, sometimes forcing people into food insecurity. Vertical farming eliminates this risk, as it is conducted indoors where farmers can control the environment.
Harsh climatic conditions such as droughts, floods, and storms have been eliminated in vertical farms. Still, yields are predicted to be high irrespective of the climatic conditions experienced in any region, making food secure in such areas.
Agricultural production has faced severe setbacks during past drought events, contributing to food inflation. However, vertical farms continue to produce high-quality crops unaffected by regional water shortages. Advanced vertical farms use closed-loop irrigation systems and controlled environments, highlighting the resilience of vertical farming.
This ability to mitigate climate risks makes vertical farming essential in regions vulnerable to extreme weather events, ensuring a stable and reliable food supply.
Integrating automation and advanced technology in vertical farming reduces the need for manual labor. Automated systems for planting, watering, harvesting, and monitoring crops streamline operations, leading to lower labor costs and increased efficiency.

Such cost-cutting measures make vertical farming economically feasible for urban agriculture, especially in regions where labor scarcity or high wages hinder the execution of traditional agriculture.
Automated vertical farms can produce thousands of heads of lettuce daily with robots handling nearly every process stage, from planting seeds to packing the final product. This high level of automation cuts labor costs and minimizes human error, resulting in consistent quality and efficiency.
In regions where agricultural labor shortages or high wages pose challenges, the cost-effectiveness of automation makes vertical farming a viable alternative to traditional methods.
Vertical farming prioritizes sustainability by minimizing resource use and environmental impact. Unlike traditional agriculture, which often depletes natural resources and contributes to deforestation, vertical farming operates in controlled environments (Controlled Environmental Agriculture, CEA) that require fewer inputs.

Vertical farms use energy-efficient LED lighting systems tailored to meet plants’ specific light requirements. Additionally, these farms often incorporate renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power to reduce their carbon footprint further.
Many vertical farms incorporate renewable energy sources like wind power to enhance sustainability further. In addition, vertical farming preserves biodiversity and natural ecosystems by preventing deforestation and excess farming.
Water scarcity is one of the leading issues worldwide. Of all freshwater consumption worldwide, agriculture uses about 70%. Vertical farming solves this problem by using hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics.
These vertical farming systems use up to 95% less water than traditional farming by recycling and recirculating water within closed-loop systems. This conservation reduces water waste and makes vertical agriculture viable in arid regions with scarce water.

Leading vertical farming companies use aeroponic technology to grow crops with minimal water. Their systems use 90% less water than required for field farming and 230 times less land, making it ideal for arid regions or areas facing water scarcity. This innovative farming method, therefore, conserves water and reduces pollution from agricultural runoff, a major contributor to waterway contamination in traditional farming systems.
Soil degradation due to over-farming, erosion, and excessive chemical use is a significant issue in traditional agriculture. Vertical farming does not use soil; instead, it opts for hydroponics and aeroponics.

Soil-based farming evasion prevents soil nutrient depletion and erosion in a vertical farm. Additionally, it helps reduce soil-borne diseases and pests, thereby attaining higher yields.
Advanced hydroponic systems prevent soil degradation, waste, and runoff while producing crops 100% free from soil contaminants, such as heavy metals or chemical residues, ensuring safer and healthier food production.
Vertical farms’ compact and modular design makes them ideal for urban areas. By growing food closer to where it is consumed, vertical farming reduces transportation costs and emissions associated with long-distance food distribution.
This proximity to urban centers also improves food freshness and quality, providing consumers with healthier options. Urban vertical farms can play a vital role in creating sustainable and self-sufficient food systems for cities.
Some urban farming companies place modular vertical farms directly inside supermarkets and restaurants. Transport is thus totally avoided, as the freshest produce goes straight to the customers while cutting emissions due to food transport.

Urban vertical farms also allow local food systems, which enable cities to take greater control of themselves and be more resilient in case of a chain break in global supply.
Food safety is a growing concern, particularly with the widespread use of pesticides and chemicals in traditional farming. Vertical farming eliminates the need for harmful pesticides by operating in sterile, controlled, naturally pest-resistant environments.

This approach ensures crops are free from toxic residues, making them safer for consumers. Additionally, the closed environments of vertical farms reduce the risk of contamination from external sources, such as polluted water or soil.
Vertical farming companies specializing in pesticide-free produce consistently meet rigorous food safety standards without pesticides. Their controlled conditions result in consistently high-quality, safe, and nutritious produce.
Traditional farming often relies on pesticides to protect crops from pests and diseases, which can harm human health and the environment. Vertical farming eliminates the need for these chemicals by maintaining pest-free growing environments.
Crops in vertical farms are grown in sealed facilities with advanced filtration systems, preventing pests from entering. This pesticide-free approach improves food safety and aligns with the growing demand for organic and sustainably produced food.
By avoiding pesticides, vertical farming reduces environmental pollution and protects ecosystems. It contributes to a healthier planet while meeting consumer expectations for clean, high-quality produce.
One of the lesser-known advantages of vertical farming is its ability to optimize crop nutritional profiles through precise environmental control. By adjusting light spectrums, nutrient solutions, and growing conditions, vertical farms can enhance vitamin content, antioxidant levels, and mineral density in crops.
Research has shown that controlled environment agriculture can increase vitamin C content in leafy greens by up to 30% compared to field-grown produce. The ability to harvest at peak ripeness and eliminate long transportation times also preserves nutritional integrity.
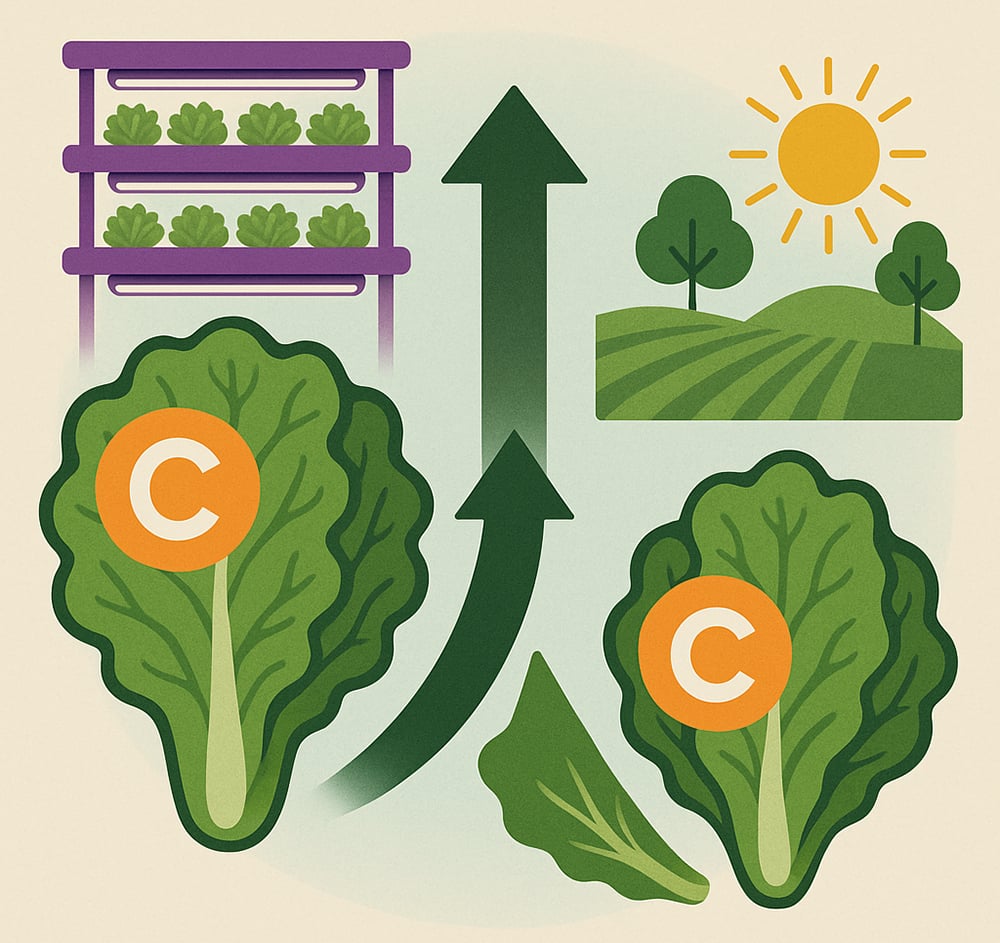
This advantage positions vertical farming as a producer of not just more food, but better food that can help address nutritional deficiencies in urban populations.
Vertical farming opens unique opportunities for growing high-value medicinal plants and functional foods that require precise growing conditions. The controlled environment is ideal for producing consistent, pharmaceutical-grade botanicals and nutraceuticals.
These specialized crops, including adaptogenic herbs, medicinal mushrooms, and plants rich in specific compounds, can command premium prices and diversify revenue streams for vertical farming operations. The sterile environment ensures purity levels required for medical applications.
This represents a significant economic advantage that traditional farming cannot easily replicate, especially for crops requiring specific environmental triggers to produce desired compounds.
Vertical farms serve as critical infrastructure for food security during natural disasters, pandemics, or supply chain disruptions. Their enclosed, controlled environments make them less vulnerable to external threats and capable of maintaining production when traditional agriculture fails.

During recent global supply chain challenges, vertical farms continued operating normally while outdoor agriculture faced numerous disruptions. This resilience makes vertical farming an essential component of emergency preparedness and national food security strategies.
Communities with local vertical farms have demonstrated greater food security during crises, highlighting the strategic importance of distributed food production systems.
Vertical farms serve as living laboratories for agricultural innovation, providing unique educational opportunities for students and researchers. These facilities allow for controlled experiments in plant biology, nutrition, automation, and sustainable technology.
Universities and research institutions are increasingly integrating vertical farming into their agricultural and engineering programs. Students gain hands-on experience with cutting-edge technology while contributing to research that advances the field.

The controlled environment allows for precise data collection and experimentation that would be impossible in traditional farming settings, accelerating agricultural innovation and workforce development.
Vertical farming provides significantly safer working conditions compared to traditional agriculture. Workers are protected from extreme weather, dangerous machinery, chemical exposure, and physical strain associated with outdoor farming.
The climate-controlled environment eliminates heat-related illnesses, while automation reduces repetitive strain injuries. The absence of pesticides and herbicides creates a healthier workplace, reducing long-term health risks for agricultural workers.
These improved working conditions help attract and retain skilled workers in agriculture, addressing labor shortage issues while promoting worker well-being and job satisfaction.

Although vertical farming has several benefits, it still has a series of challenges attached to it. Here are the potential disadvantages:
Vertical farming is changing the way people farm. It is a transformation approach that provides several solutions to farmers’ daily challenges. These include year-round food production, growing crops in urban areas, and revolutionizing food growing in general to improve global food security for generations.

If you’d like to learn more about vertical farming or what monitoring kits we offer commonly used in vertical farming systems, please don’t hesitate to contact the world-class team at Atlas Scientific.

Finding the best pH probe for hydroponics can make or break your growing success. In hydroponics, maintaining the correct pH is essential because it directly

The fastest way to reduce ammonia levels in a fish tank is to perform partial water changes, temporarily stop feeding fish, use chemical filtration, increase
Notifications