

What Is The Wick System In Hydroponics?
With no need for pumps or electricity, a hydroponic wick system is a straightforward, passive growing technique that transfers nutrient solution from a reservoir to
# Type at least 1 character to search # Hit enter to search or ESC to close

No products in the cart.

No products in the cart.
Product Categories

Water covers around 71% of the Earth’s surface, and one of the main issues we are facing today is water pollution. We must reduce water pollution, which is why there are many solutions to combat the problem.
Sometimes water becomes polluted with chemicals such as oil, harmful bacteria, and other microorganisms. When water becomes polluted, water quality is reduced, often becoming toxic, negatively affecting animals, plants, and the environment. Just because you cannot see the problem or it disappears, it doesn’t mean that it just vanishes.
The best solution to prevent water pollution is to stop it at the source. Luckily, there are many solutions in reducing water pollution such as wastewater treatments, stormwater management, and water conservation.
In this article, we are going to cover what water pollution is, solutions to combat the issue, and how to measure water quality.
Water pollution is the contamination of any water system or body, from lakes and oceans to groundwater. We are well aware of water pollution issues thanks to media coverage, especially as we are still producing harmful chemicals that find their way into our waters.
When water becomes contaminated, it has detrimental effects on both animals and plants (who rely on uncontaminated water), and the sensitive water environment.
Global warming is increasing, and it is an issue we cannot turn a blind eye to. With climate change and global warming, our precious planet is starting to edge towards a water crisis. Our global population is increasing, putting demand on water availability, and because of this, we are seeing an increase in waterborne diseases due to our waters becoming polluted.
To find solutions to the water pollution issue, we must understand what causes it in the first place. Causes of water pollution can be anything from overdevelopment to inappropriate sewage disposal.
Once the cause of water pollution is identified, solutions can be made to combat the issue.
Water pollution can come from any of the following:
There is no single or simple answer to stop the water pollution crisis, however, there are many solutions to prevent water pollution both in our daily lives and within industries.
We can separate the issue with water pollution into 10 notable solutions:
Treating water before it enters the waterway system is probably the most efficient way of reducing water pollution – hitting the issue right at the source!
Wastewater treatment facilities have the technology and tools to remove most pollutants through biological, physical, and chemical processes. For example, sewage treatments allow water to travel through different sanitization chambers to reduce toxic levels of water pollutants and prevent leakages into water systems.
To ensure that wastewater treatments function properly, regular maintenance of equipment is required. This includes applications such as water treatment sensors, which are vital to measure and remove contaminants to reduce water pollution.
Water treatment sensors:
Plastic waste is a huge issue. More than 8 tonnes of plastic enters our ocean every year, plus the plastic is to outweigh the number of fish by 2050, these facts are shocking! Plastic waste also decays water supplies. This is why it is extremely important to reduce plastic waste and improve sustainability both locally and globally.
Plastic bottles and bags get most of the media coverage, but plastics are entering water systems in ways you cannot always see, and are most likely not aware of.
Microplastics are a major issue and are found in:
To reduce plastic waste at home, we can do the following:
Do you turn the tap off when brushing your teeth, or between shampooing your hair in the shower?
Water is a scarce resource, so limiting the amount of water you use daily will contribute to reducing water pollution.
Toilets used to use ~3.5 gallons of water per flush, however, the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) enforced the rule that all toilets must only flush 1.6 gallons of water, per flush.
Most houses are now being built with toilets that have 2 buttons, one for a small flush (0.8-1.1 gallons of water), and one for full power (1.6 gallons of water). Water-efficient toilets are one step in the right direction to conserve water and reduce water pollution.
Having a water-efficient toilet will also save you money!
Septic tanks are a great way to efficiently treat sewage; separating solids from liquid. Septic tanks degrade solids and allow liquid to flow into drainage systems via biological processes.
Using septic tanks reduces water pollution by removing pollutants already present in water.
Your toilet is not a trash bin, it is for human waste only. Avoid flushing wet wipes, diapers, and other things that cross your mind down the toilet – that is what a trash bin is for.
Flushing these items down the toilet can cause sewage lines to become blocked, therefore the sewage system cannot do its job properly. When things get blocked, water cannot be cleaned efficiently in wastewater facilities or a septic tank.
Another way we can combat water pollution is to manage stormwater where possible. Stormwater flows along the road and other surfaces, which can collect viruses, bacteria, and other harmful pollutants, which then make their way into drains, rivers, and eventually the ocean.
Treatment and management of stormwater vary from reverse osmosis (RO), advanced oxidation, and sand filtration.

Agriculture is a trillion-dollar industry worldwide, using up to 70% of surface water supplies to meet the demand of livestock production and farming.
As agriculture is such a large industry, it is one of the primary causes of water pollution. When it rains, runoff transports pesticides and fertilizers.
Agriculture can be environmentally friendly, known as green agriculture. Green agriculture involves using pesticides and fertilizers that contain no harmful chemicals. It also includes planting trees and creating wetlands to form buffer zones, which filter runoff and water pollutants.
When nitrate levels are high in water, it creates the perfect environment for eutrophication or overfertilization from runoff to occur. This allows algae and phytoplankton in the water to rapidly grow, reducing water quality, and contributing to the water pollution issue.
Denitrification is directly converting nitrates into nitrogen gas. This ecological process prevents nitrate leaching into soils and helps reduce groundwater contamination.
Although this is also a wastewater treatment, it goes through a different process to regular wastewater systems, which is why it is important to also note.
Ozone wastewater treatment uses an ozone generator to break down water pollutants. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation or an electric discharge field inside the generator converts oxygen into ozone. This process oxidizes bacteria, organic matter, and other water pollutants.
There are also solutions you can personally do to reduce water pollution:
Testing and measuring water quality tells us if water bodies are polluted. Testing water quality is one of the most important ways to protect sensitive aquatic environments and support clean water for a diversity of plants and animals, including humans.
There are many ways and to measure water quality that covers a wide variety of parameters such as pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), ORP, and temperature.
There are 7 ways we can test water quality and reduce water pollution:
CDOM (colored dissolved organic matter) is naturally found in water bodies. UV light is absorbed by the organic matter which decomposes releasing the organic pollutant tannin, turning water murky. Tannin is related to decreasing pH and depleting oxygen levels in the water. When CDOM fluoresces, it is known as fluorescent dissolved organic matter (FDOM).
Electrical optical sensors are used to measure CDOM/FDOM. They measure light availability and dissolved organic matter (DOM) concentrations.
When eutrophication occurs in water bodies, oxygen levels become depleted and nitrogen and phosphorus levels increase, creating a toxic environment for both plants and animals. Measuring algal growth and water quality contributes to reducing water pollution.
Chlorophyll fluorescence is measured with algae toximeters which records both the wet-chemical and active chlorophyll percentages.
Conductivity in the water tells us the water quality and also affects the salinity and TDS (total dissolved solids) of water. Analyzing water quality can be measured with conductivity, salinity, and TDS meters.
Even though each meter measures different water parameters, the results are collaborated to indicate how much water pollution is present.
Temperature is an important water quality parameter to measure as it affects other parameters in water systems.
There is a wide variety of thermometers and temperature probes and sensors to record accurate readings.
It is important to measure DO in wastewater treatments and water bodies as DO levels less than 6mg/L can be toxic to aquatic ecosystems.
DO electrochemical sensors are most commonly used, however, an optical DO sensor, colorimetric method, or Winkler titration method can also be used.
pH fluctuations can be extremely dangerous in aquatic systems; a safe aquatic environment has a pH between 6.0 and 8.0. Many factors can change pH in aquatic systems, quickly creating toxic environments.
pH can be tested using colorimetric or electrochemical methods.
Colorimetric methods include pH indicators and litmus test papers. These are easy to use and are cheap, however for accurate pH readings, investing in electrochemical methods such as a pH meter is highly recommended. You must calibrate a pH meter before using it.
You can find more information on pH sensors and the different applications they are used for here.
Turbidity is how murky water becomes, and is an essential test for water quality. TSS (total suspended solids) and decaying matter from animals and plants change turbidity levels, often reducing how much light is penetrated through the water.
Sudden increases in turbidity are an indication of water pollution, usually caused by an influx of heavy metals and other effluents.
The simplest way to measure turbidity is either a turbidity tube or Secchi disk, but for more accurate measurements a turbidity meter is recommended.
Water pollution is an issue we are currently facing which is why solutions must be made to conserve aquatic environments, protect human health, and other animals (& plants) that are dependent on water systems.
Testing different water parameters will determine the water quality so that water pollution can be identified.
If you would like to know more about what water testing kits we have to offer, feel free to reach out to one of our staff at Atlas Scientific, part of our world-class team. We look forward to answering any questions that you may have.
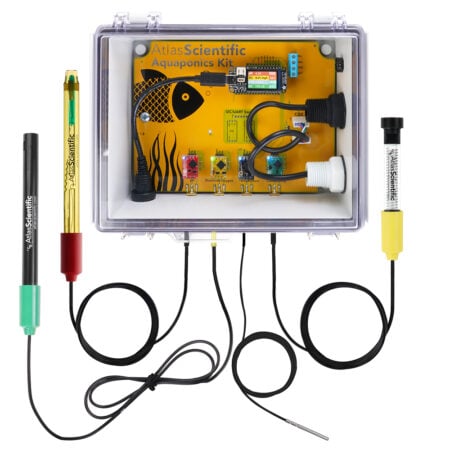


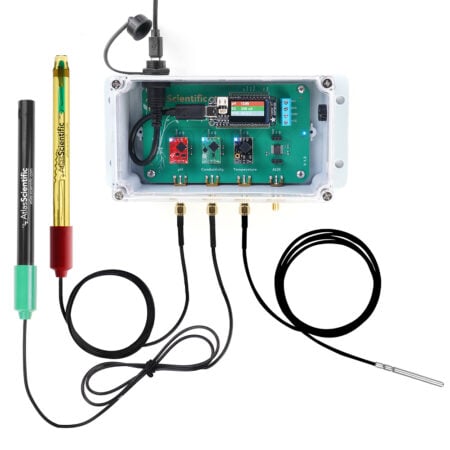
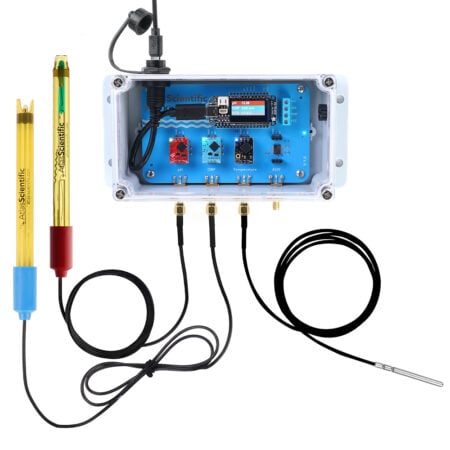

With no need for pumps or electricity, a hydroponic wick system is a straightforward, passive growing technique that transfers nutrient solution from a reservoir to

The best plants for hydroponics include fast-growing leafy greens, flavorful herbs, and self-pollinating fruiting crops that thrive in soilless systems, offering higher yields, efficient water