

Best pH Probes For Hydroponics in 2025 – A Complete Buying Guide
Finding the best pH probe for hydroponics can make or break your growing success. In hydroponics, maintaining the correct pH is essential because it directly
# Type at least 1 character to search # Hit enter to search or ESC to close

No products in the cart.

No products in the cart.
Product Categories

To calibrate a DO meter, start by rinsing the probe with distilled water to remove any residue or contaminants. Then, immerse the probe in the zero oxygen solution, allow it to stabilize for a few minutes, and adjust the reading on the meter to zero. Next, immerse the probe in the high-oxygen solution and allow it to stabilize, adjust the reading on the meter to match the known value of the high-oxygen solution.
Dissolved oxygen (DO) refers to the amount of oxygen gas that is dissolved in water. It plays a vital role in supporting the survival of various organisms, especially fish and other aquatic organisms that rely on oxygen for respiration. Dissolved oxygen levels can vary depending on various factors such as temperature, salinity, and the presence of plant life.
A DO meter is a vital tool used in various industries, such as wastewater treatment plants, aquaculture, and environmental monitoring (water quality). It provides valuable information about the health and quality of water, which is crucial for maintaining optimal conditions for aquatic life.
Dissolved oxygen plays a crucial role in various industries, including the following:

Dissolved oxygen levels indicate the degree of oxygen saturation in water, which directly affects the efficiency of biological processes used to treat wastewater. By measuring dissolved oxygen, operators can ensure that enough oxygen is present for the microorganisms to break down organic matter effectively.
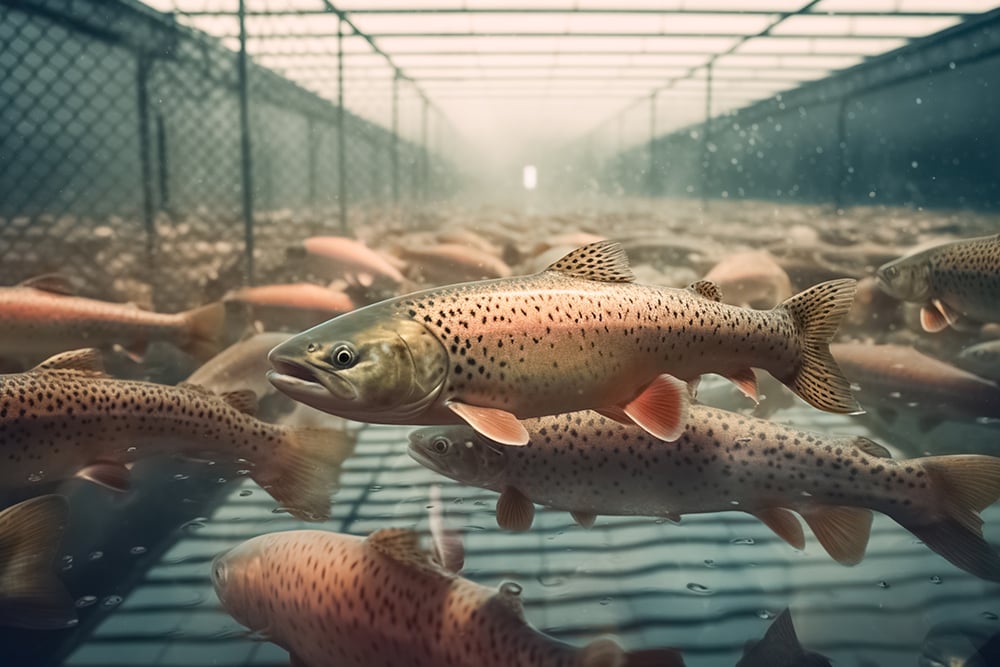

In fish farms, dissolved oxygen levels need to be monitored closely to ensure optimal conditions for fish health and growth. Fish rely on dissolved oxygen in the water to breathe, and insufficient levels can lead to stress, reduced growth rates, and even death. By regularly measuring dissolved oxygen, fish farmers can adjust aeration systems or other processes to maintain suitable oxygen levels and create a healthy environment for their aquatic livestock.

During the fermentation process, yeast converts sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide. Dissolved oxygen can negatively affect this process by promoting the growth of spoilage microorganisms or oxidizing compounds in the beer and in wine, resulting in off-flavors and reduced shelf life. By monitoring dissolved oxygen levels throughout the brewing process, brewers can ensure the production of high-quality beer with excellent taste and a longer shelf life.
A dissolved oxygen meter (DO meter) is a device used to measure the amount of oxygen dissolved in a liquid, such as water. It is an essential tool in various industries and fields, including environmental monitoring ( for example agriculture, aquaponics & hydroponics), aquaculture, and wastewater treatments.

The DO meter works by utilizing an electrochemical sensor that measures the oxygen concentration in the liquid sample. It consists of a dissolved oxygen probe that is inserted into the liquid and connected to a handheld or portable device that displays the readings. The probe contains a cathode and an anode separated by a membrane, which allows the diffusion of oxygen molecules while preventing other substances from interfering with the measurement.
There are three main types of dissolved oxygen meters:
Handheld DO Meters: This type of dissolved oxygen meter is compact, portable, and user-friendly. These meters are commonly used in environmental studies, aquaculture, and water treatment facilities.
Benchtop DO Meters: This meter is larger and designed for more advanced laboratory use. These meters are often used in research laboratories and quality control settings where precise measurements are required.
Inline DO Meters: These meters can be installed directly into a pipeline or tank for continuous monitoring. These meters are commonly used in industries such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment plants.
The calibration process involves verifying the accuracy of the DO meter by comparing its readings to known reference values. This ensures that the instrument is functioning correctly and provides reliable measurements. Calibration also takes into account factors that can affect the accuracy of the readings, such as temperature, salinity, and atmospheric pressure.
By calibrating the DO meter, any deviations or drifts in its performance can be identified and corrected, guaranteeing accurate measurements. Without regular calibration, the readings provided by a DO meter may become inaccurate, leading to potential errors in data analysis and decision-making.
Regular calibration of a DO meter helps to maintain the instrument’s accuracy over time. Environmental factors and normal wear and tear can cause slight changes in the meter’s performance. By calibrating at regular intervals, these changes can be detected early on, preventing any significant deviations in accuracy. This is particularly important when working with sensitive ecosystems or when compliance with specific regulatory standards is required.
In addition to ensuring accuracy, calibrating a DO meter also enhances its longevity. Over time, the sensor in the DO meter may become fouled or contaminated, affecting its performance. Regular calibration allows for sensor cleaning and maintenance, which can prolong the life of the DO meter, particularly the electrodes in the DO probe. It also provides an opportunity to check for any physical damage or malfunction that may require repair or replacement.

Calibrating a DO meter may seem daunting at first, but by following our simple step-by-step process, it can be done effectively and efficiently.
The frequency of calibrating your DO meter depends on various factors, including the manufacturer’s recommendations, the specific application of the meter, and the environmental conditions in which it is used. In general, it is advisable to calibrate your DO meter at regular intervals to ensure accurate measurements.
For most applications, calibrating the DO meter once every month or every few weeks is recommended. However, if the meter is subjected to harsh or demanding conditions, such as continuous use in high-temperature environments or exposure to chemicals, more frequent calibration may be necessary.
Improper Electrode Maintenance: The electrode of a DO meter is highly sensitive and can easily become contaminated or damaged. If the electrode is not properly cleaned and stored after each use, it can lead to inaccurate readings during calibration. To avoid this issue, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for electrode maintenance and to regularly clean and calibrate the electrode.
Incorrect Calibration Solutions: If the wrong calibration solution is used or if the solution is expired or contaminated, it can lead to inaccurate readings. It is important to use the correct calibration solution for your specific DO meter and to ensure that it is not expired or contaminated before using it for calibration.
Temperature Variations: Dissolved oxygen measurements are temperature-dependent, and temperature changes can affect the accuracy of the readings. If the temperature of the calibration solution is not controlled during calibration, it can lead to inaccurate readings. It is therefore important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for temperature control during calibration, and to allow sufficient time for the calibration solution to reach the desired temperature before starting the calibration process.
Air Bubble Formation: Air bubbles can become trapped around the electrode, preventing accurate measurements during calibration. To avoid this issue, it is important to properly degas the calibration solution before use and to ensure that no air bubbles are present around the electrode. This can be done by gently stirring the calibration solution or by using a degassing apparatus.
[air-bubbles-under-dissolved-oxygen-probe.jpg]
Electrode Drift: This refers to a gradual change in the electrode’s response over time, leading to inaccurate readings. This can be caused by factors such as aging electrodes or exposure to chemicals or contaminants. To minimize electrode drift, it is important to regularly calibrate and maintain the DO meter, and replace electrodes periodically.
Most DO meters are calibrated at a standard temperature of 25 degrees Celsius. This is because 25 degrees Celsius is considered the average temperature for most aquatic environments. Calibrating at this temperature allows for more accurate readings and ensures that the DO meter is properly calibrated to provide reliable data.
However, it is important to note that some DO meters may have different calibration temperature options, so it is always important to consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific guidance on calibration temperatures.
Calibrating a dissolved oxygen (DO) meter is a critical step in obtaining accurate and reliable measurements. By following the proper calibration procedures, using certified calibration solutions, and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure that your DO meter provides precise readings.
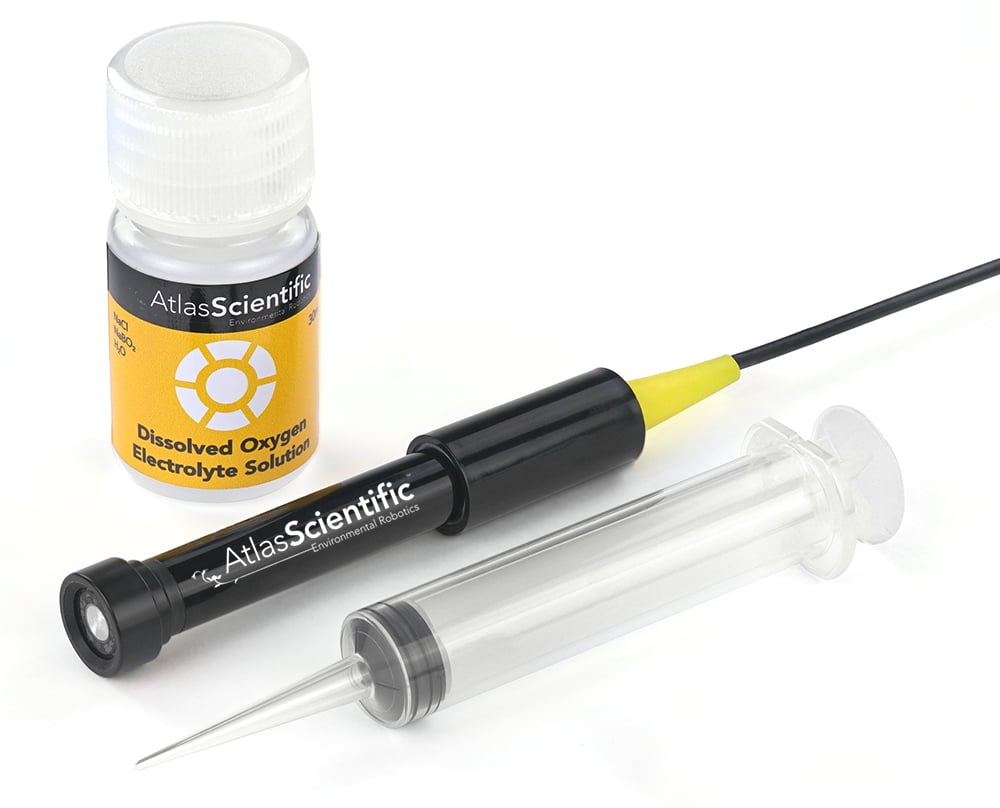
If you have any questions regarding DO calibration or which DO meter will best suit your testing needs, do not hesitate to contact the world-class team at Atlas Scientific.







Finding the best pH probe for hydroponics can make or break your growing success. In hydroponics, maintaining the correct pH is essential because it directly

The fastest way to reduce ammonia levels in a fish tank is to perform partial water changes, temporarily stop feeding fish, use chemical filtration, increase